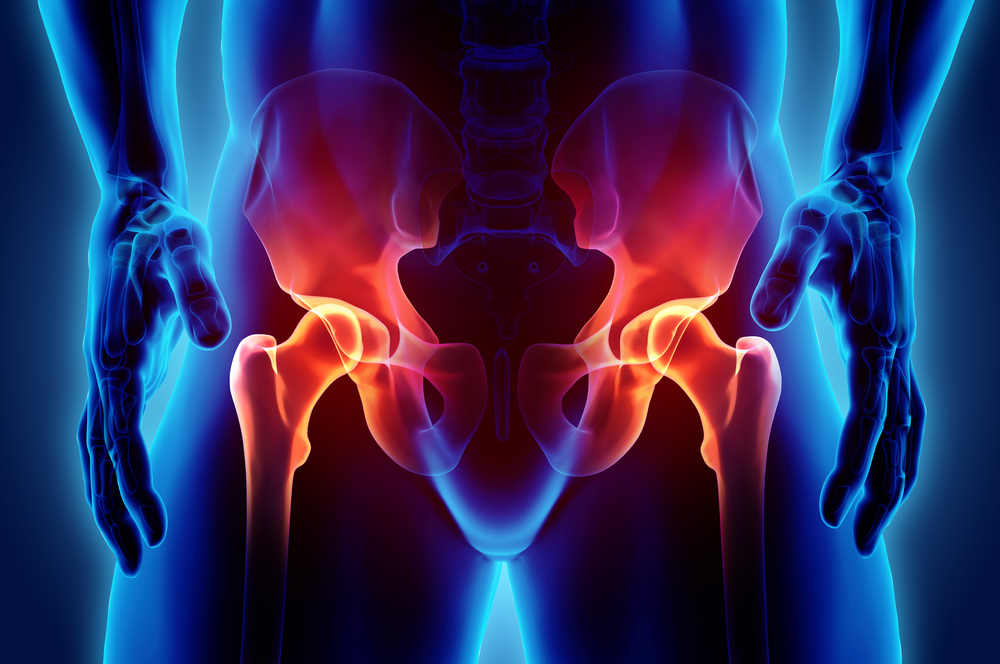
Sacroiliac (SI) joint dysfunction refers to pain and inflammation in the SI joints, located where the spine and pelvis connect. Understanding the causes and symptoms of this surprisingly common condition can help patients find relief.
Nearly 15-30% of lower back pain cases stem from SI joint problems. And as we age, wear and tear or injuries can lead to more pronounced dysfunction. By learning about the anatomy, purpose, and causes of SI issues, patients can better communicate with their doctor and explore personalized treatment options.
What is the Sacroiliac Joint?
The sacroiliac joints are located deep in the lower back, where the triangular sacrum bone and wing-shaped ilium bones of the pelvis meet. There are two SI joints, one on each side of the sacrum. These unique joints have several key features:
- Uneven Surfaces: The SI joints resemble puzzle pieces, with many nooks and ridges that fit tightly together to provide stability.
- Strong Ligaments: Dense ligaments span the SI joints, limiting movement but providing flexibility.
- Cartilage Layer: A smooth cartilage coating over the bone surfaces acts as a shock absorber.
- Fluid-Filled Spaces: The SI joints also contain synovial fluid, which lubricates the bones and allows slight rotation or compression.
Overall, the SI joints play a vital role in dissipating weight, absorbing shock, and maintaining balance across the pelvis and lower spine. Dysfunction can occur following injuries, inflammatory conditions, or mechanical factors over time.
Causes of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
There are several potential causes and risk factors for SI pain and inflammation. By understanding the source, patients can better manage irritation. Common causes include:
Osteoarthritis
Over time, the cartilage lining the SI joints can wear away, eventually resulting in bone-on-bone contact. This causes inflammation, stiffness, and osteoarthritic changes. Excess weight gain and aging raise osteoarthritis risks. Prior injuries may also accelerate joint degeneration later in life.
Inflammatory Arthritis
Various inflammatory joint diseases can affect the SI region, including ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and reactive arthritis. With inflammation, the immune system attacks healthy tissue, leading to progressive joint damage if left untreated. Genetics and environmental factors often contribute.
Injury/Trauma
Direct blows to the pelvis through falls, accidents, or sports can injure ligaments around the SI joints. Fractures alongside the joint may also accelerate wear. Sudden impact forces or whiplash can misalign the sacrum and ilium as well.
Pregnancy
Fluctuating hormones during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum can irritate SI joints in some women. The hormone relaxin prepares joints and ligaments for delivery but also increases mobility. Added weight and pressure further strain the region.
Leg Length Differences
If one leg is markedly shorter, patients often walk with an exaggerated tilt of the pelvis. This angled, uneven gait can essentially twist or overwork one SI joint over time, causing gradual irritation.
Symptoms of Sacroiliac Dysfunction
The most common symptom involves lower back, buttock, hip or groin pain on one side. This discomfort often flares up or intensifies when standing from sitting or climbing stairs. Additional symptoms may include:
- Sharp, dull, aching, or “deep” unilateral pain
- Pain radiating down the leg (sciatica-like)
- Joint stiffness and reduced mobility
- Sensations of pelvic instability or buckling
- Aggravated symptoms when running, bending, or weight-bearing
Since many surrounding structures share nerves, SI inflammation can mimic similar issues like herniated discs or hip bursitis as well. Identifying the exact pain generator requires a detailed medical history, physical exam, and possible imaging.
Diagnosing Sacroiliac Dysfunction
Given the complex network of muscles, joints, and nerves in the region, diagnosing the exact source of pain can prove challenging. Doctors utilize a combination of strategies, including:
- Medical History: Discussing symptom duration, onset, relieving/aggravating factors.
- Physical Examination: Palpating and moving the joint to assess pain response. Checking leg lengths.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays to assess joint alignment or osteoarthritis. MRI scans visualizing soft tissues.
- Diagnostic Injections: Injecting numbing agent to confirm SI joint as pain source.
Based on test results and the pattern of symptoms, physicians can determine optimal treatment paths for each patient.
Treatment Options
The good news is there are many conservative treatment options for managing SI dysfunction. Most patients improve through a combination of lifestyle changes, therapy, and medication management:
Lifestyle Changes
- Weight loss to reduce joint pressures
- Physical therapy exercises strengthening stabilizer muscles
- Preventive bracing or supportive footwear
- Improving posture, flexibility, core strength
- Avoiding provocative activities initially
Medications
Anti-inflammatories like NSAIDs or short-term steroids help relieve swelling and discomfort. Muscle relaxants ease spasms.
Injections
- Steroid injections directly into joint space
- Prolotherapy tightening up ligaments
- Radiofrequency ablation deactivating local nerves
Surgery
If joint instability or arthritis is severe, SI joint fusion procedures can realign and stabilize the region by fusing the bones.
Conclusion
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a relatively common source of back/pelvic pain, caused by arthritis, injuries, woven mechanics or pregnancy. Diagnosing the exact structure involved is key. Most patients improve through conservative treatment approaches above, alongside communicative doctor visits guiding symptom management. By understanding the anatomy, purpose, and dysfunction of the SI joints, patients can better advocate for their health during the healing process.
Written by Dr. Tony Mork
Orthopedic Spine Surgeon
I’m Dr. Tony Mork, MD, a Minimally Invasive Orthopedic Spine Surgery Specialist in Newport Beach, California. With over 40 years of experience, I’m dedicated to providing information for all topics that involve neck and back pain.
February 1, 2024
Contact a Spine Specialist Near You!
Related Articles
Lower Back Pain | An Overview
Lower back pain is an exceedingly common affliction that affects up to 80% of adults at some point in their lives. Understanding the underlying causes of lower back pain is key to finding the appropriate treatment and relief. Anatomy of the Lower Back The lower back,...
Degenerative Disc Disease | Causes and Risk Factors
Degenerative disc disease describes age-related wear and tear to the rubbery spinal discs cushioning the vertebrae that can lead to chronic back or neck pain. While partly genetic, there are also lifestyle factors and injuries that accelerate disc degeneration over...
Upper (Thoracic) Back Pain | What is Causing My Pain?
Upper back pain is a surprisingly common affliction, affecting up to one-quarter of the adult population at some point. While not as prevalent as lower back pain, discomfort in the thoracic region still accounts for a substantial slice of musculoskeletal complaints...